In a once-sleepy Ukrainian village north of Kyiv, Mykola Moroz, nicknamed Kolia, answered his doorbell in the early months after Russia’s 2022 full-scale invasion to find two Russian soldiers and their commander ready to take him into custody. As Kolia’s wife watched in horror, they put a bag over her husband’s head and dragged him...
World
Inside Bashar Assad’s Detention Centers, Where ‘Death Was the Least Bad Thing’
Handcuffed and squatting on the floor, Abdullah Zahra saw smoke rising from his cellmate’s flesh as his torturers gave him electric shocks. Then it was Zahra’s turn. They hanged the 20-year-old university student from his wrists until his toes barely touched the floor and electrocuted and beat him for two hours. They made his father watch...
Study Reveals Oldest-Known Evolutionary “Arms Race”
Hundreds of punctured shells from the Cambrian illuminate unique predator-prey interactions in the ocean 517 million years ago A new study led by researchers at the American Museum of Natural History presents the oldest known example in the fossil record of an evolutionary arms race. These 517-million-year-old predator-prey interactions occurred in the ocean covering what...
A River Route for Food and Crime: The Dual Nature of a Major South American Waterway
From its headwaters in Brazil, the Paraguay River flows hundreds of miles (kilometers) south to where it joins the Parana River to form a single 2,100-mile (3,400-kilometer) waterway that carries much of the agricultural and mineral wealth of South America to the Atlantic. The riverine waterway connects Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay and carries...
Nigerian Agency ‘Failed Completely’ to Clean Up Oil Damage Despite Funding, Leaked Files Say
As it passed above the Niger Delta in 2021, a satellite took an image. It showed acres of land, scraped bare. The site, outside the city of Port Harcourt, was on a cleanup list kept by the United Nations Environment Programme, supposed to be restored to green farmland as the Delta was before thousands of...
Human-Related Activities Continue to Threaten Global Climate and Productivity
The pace at which anthropogenic climate change has altered the terrestrial carbon stores is making our current climate-change mitigation efforts seem fruitless, unless behaviors are quickly changed. Climate change induced by human behaviors, or anthropogenic climate change, has been a hot topic for decades and is not going away. As with any problem, reviewing datasets...
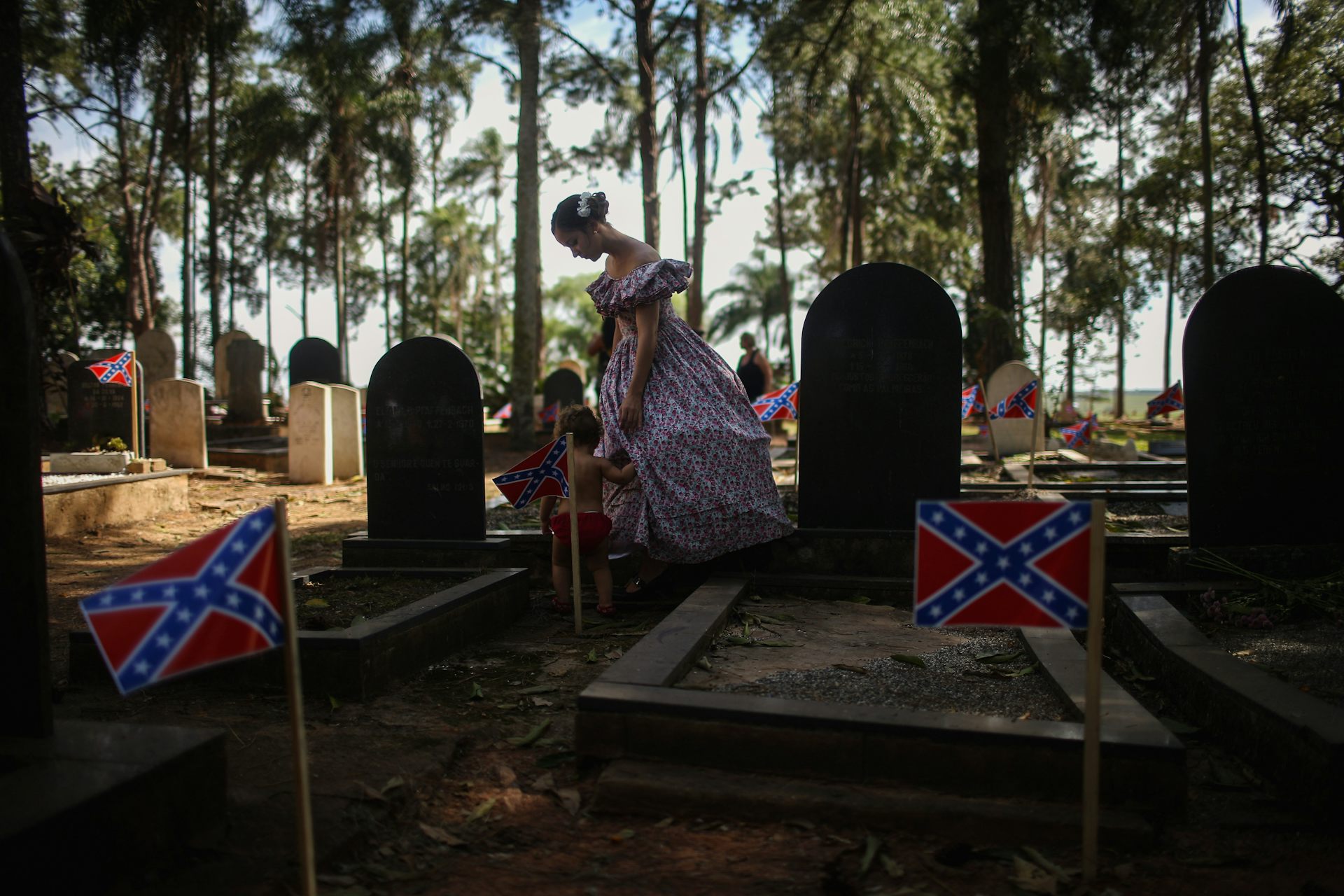
How a Small Brazilian Town Became an Unlikely Battleground Over Confederate Memory
There were no antebellum hoop skirts at the site of Brazil’s annual “Festa Confederada,” or Confederate Festival, in 2024. Flag poles that once flew the Brazilian flag alongside the red, white and blue rebel banner of the American Confederacy stood barren. Since 1980, the Confederate Festival – a series of cultural performances and culinary experiences...
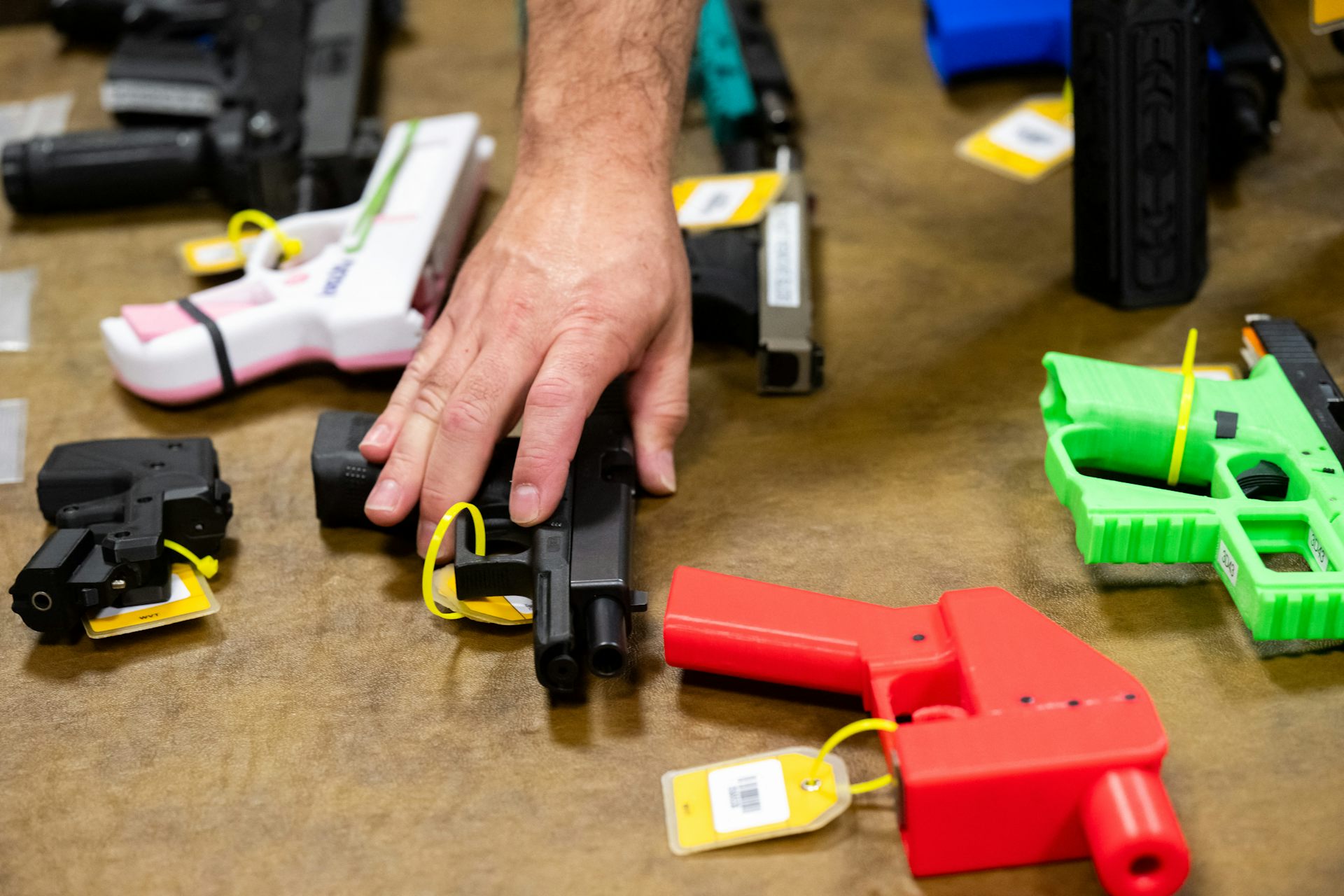
3D-Printed Guns, Like the One Allegedly Used to Kill a Health Care CEO, Are a Growing Threat in the U.S. and Around the World
Police investigating the shooting of UnitedHealthcare CEO Brian Thompson on Dec. 4, 2024, have announced that the suspected assailant had used a 3D-printed gun. Several high-profile crimes in recent years have involved this kind of homemade, or partially homemade, weapon. Often called “ghost guns” because they can be hard to trace, these firearms can be...
Marco Rubio Is No Friend of Havana − but Does Trump’s Pick for Secretary of State Mean Cuba Policy Is Set?
The U.S. looks set to have its first-ever Cuban American secretary of state in 2025, after President-elect Donald Trump nominated U.S. Sen. Marco Rubio of Florida for the role. But don’t expect that to mean cozier relations between Havana and Washington. Rubio, who if confirmed by the Senate will also be the first Latino to...
In Nigeria’s Lithium Boom, Many Mines Are Illegal and Children Do Much of the Work
Dressed in a faded pink dress, 6-year-old Juliet Samaniya squats under scorching skies to chip at a jagged white rock with a stone tool. Dust coats her tiny hands and her hair as she works hour after hour for less than a dollar a day. The landscape around her is dotted with active and abandoned...