Researchers have developed a human cell ‘membrane on a chip’ that allows continuous monitoring of how drugs and infectious agents interact with our cells, and may soon be used to test potential drug candidates for COVID-19. The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, Cornell University and Stanford University, say their device could mimic any cell...
Health
35% of Excess Deaths in Pandemic’s Early Months Tied to Causes Other Than COVID-19
Since COVID-19’s spread to the United States earlier this year, death rates in the U.S. have risen significantly. But deaths attributed to COVID-19 only account for about two-thirds of the increase in March and April, according to a study published Wednesday in the Journal of the American Medical Association. Researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University and...
Growing Numbers of Alcohol Related Hospital Admissions Linked to Local Spending Cuts
According to the researchers, the study shows that spending cuts to alcohol services represent a false economy since decreases in expenditure are linked to increased hospital admissions which inevitably are costly to society and the economy. In March 2012 the Health and Social Care Act (HSCA) transferred the responsibilities of commissioning specialist drug and alcohol...
Respiratory Droplet Motion, Evaporation and Spread of COVID-19-Type Pandemics
It is well established that the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for the COVID-19 disease is transmitted via respiratory droplets that infected people eject when they cough, sneeze or talk. Consequently, much research targets better understanding droplet motion and evaporation to understand transmission more deeply. In a paper in Physics of Fluids, researchers developed a mathematical model, proceeding from...
Face Mask Construction, Materials Matter for Containing Coughing, Sneezing Droplets
While the use of face masks in public has been widely recommended by public health officials during the current COVID-19 pandemic, there are relatively few specific guidelines pertaining to mask materials and designs. A study from Florida Atlantic University, in the Physics of Fluids, looks to better understand which types are best for controlling respiratory droplets...
Lifetime Discrimination May Increase Risk of Hypertension Among African Americans
Lifetime discrimination is a chronic stressor that may increase the risk for hypertension also known as high blood pressure, in African Americans, according to new research published today in Hypertension, an American Heart Association journal. “Previous studies have shown that discrimination affects African Americans’ health; however, this research is one of the first large, community-based studies...
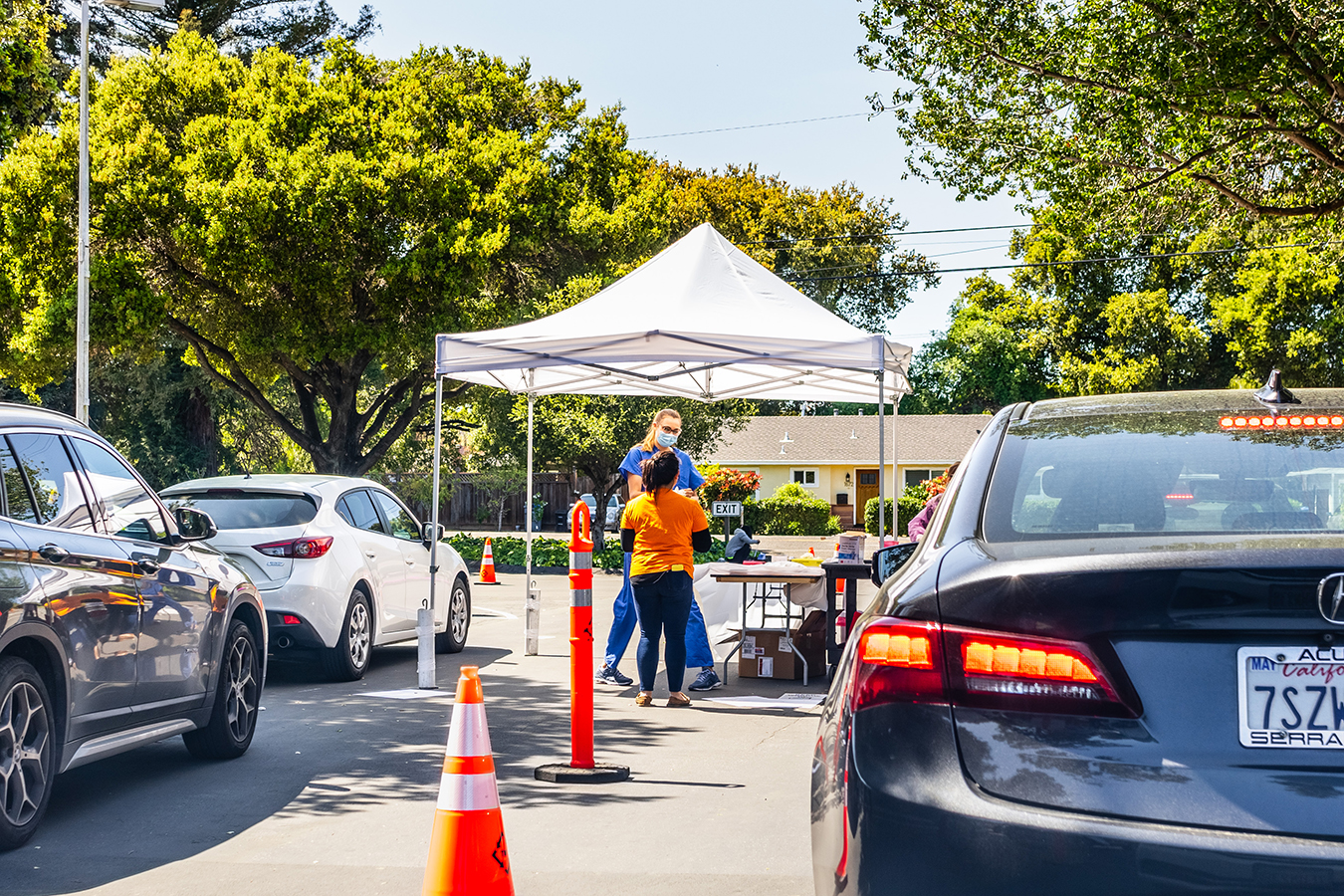
As Cases Spike, California Pauses Multimillion-Dollar Testing Expansion
In April, Gov. Gavin Newsom launched a multimillion-dollar state initiative to bring COVID-19 testing to the people and places with the least access: rural towns and disadvantaged inner-city neighborhoods. California is now halting its expansion, citing costs, even as the state is getting walloped by record-setting spikes in new infections and double-digit increases in hospitalizations....
Long-Term Use of Muscle Relaxants Has Skyrocketed Since 2005
Office visits for ongoing prescribing of skeletal muscle relaxant drugs tripled from 2005 to 2016, according to a new study from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Moreover, in 2016, nearly 70 percent of patients prescribed muscle relaxants were simultaneously prescribed an opioid — a combination that has the...
Gas Cooker Exposure Can Lower Blood Pressure
The study, published recently in Circulation Research and led by a team from King’s College London, has investigated how nitrogen dioxide can impact the cardiovascular system. The study examined the blood chemistry and cardiovascular changes of 12 healthy volunteers. They sat next to a domestic gas cooker for ninety minutes followed by ninety minutes with normal background...
Children More Resilient Against Coronavirus
The majority of children with COVID-19 in 26 countries fared well clinically compared to adults during the first four months of the pandemic, a newly released study shows. Researchers from the Long School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio prepared the study, which is the largest systematic review...