A new study of beliefs and attitudes toward COVID-19 in five different countries – UK, US, Ireland, Mexico and Spain – has identified how much traction some prominent conspiracy theories have within these populations. The research reveals “key predictors” for susceptibility to fake pandemic news, and finds that a small increase in the perceived reliability...
Health
Experiencing Police Violence Worsens Mental Health in Distinct Ways
The experience of police violence is associated with mental and emotional trauma distinct from that caused by other kinds of violence, creating a public health crisis for communities most affected. Simply put, the experience of police violence puts Black, Latino, Indigenous, and sexual minority communities at higher risk of distinct mental health problems, in addition...
Total Deaths Recorded During the Pandemic Far Exceed Those Attributed to COVID-19
For every two deaths attributed to COVID-19 in the U.S., a third American dies as a result of the pandemic, according to new data published October 12 in the Journal of the American Medical Association. The study, led by researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University, shows that deaths between March 1 and Aug. 1 increased 20%...
Clinical Study Aims to Better Understand COVID-19 Immunity
People who have recovered from COVID-19, and their close contacts, could hold the key to understanding how immunity to the disease develops, how long it lasts and what happens when immunity is lost. The COVID PROFILE study, led by the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute, will use blood samples from people in Victoria to look...
Pandemic-Related Stress Leads to Less Employee Engagement
As COVID-19 cases surged this spring, the pandemic led some people more than others to ponder their own mortality. A new study in China and the United States suggests that these people were the ones who showed the highest levels of stress and the least engagement at work. But the research also uncovered a bright...
COVID-19: Examining Theories for Africa’s Low Death Rate
As the threat of a COVID-19 pandemic emerged earlier this year, many felt a sense of apprehension about what would happen when it reached Africa. Concerns over the combination of overstretched and underfunded health systems and the existing load of infectious and non-infectious diseases often led to it being talked about in apocalyptic terms. However,...
Mask Mandates Shown to Significantly Reduce Spread of COVID-19
A new study by Simon Fraser University (SFU) researchers has found clear evidence that wearing a mask can have a significant impact on the spread of COVID-19. The researchers, from SFU’s Department of Economics, have determined that mask mandates are associated with a 25 percent or larger weekly reduction in COVID-19 cases. The finding of...
Every COVID-19 Case Seems Different; These Scientists Want to Know Why
As scientists around the world develop life-saving COVID-19 vaccines and therapies, many are still wondering exactly why the disease proves deadly in some people and mild in others. To solve this puzzle, scientists need an in-depth understanding of how the body’s many types of immune cells respond to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. A...
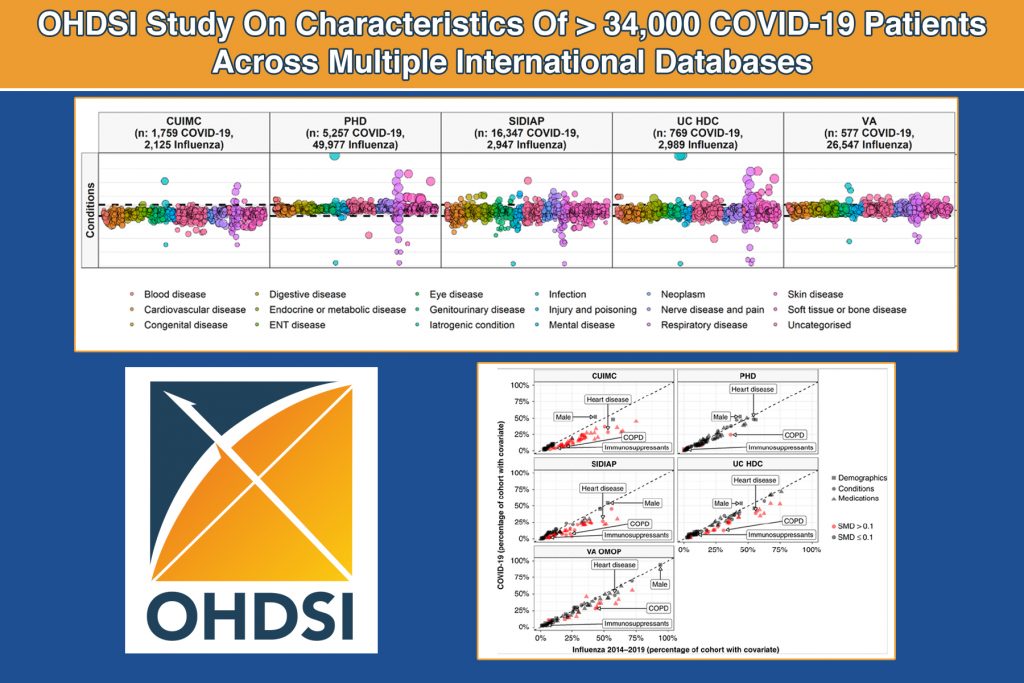
Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Are Younger, Healthier Than Influenza Patients
Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 were more likely male, younger, and, in both the US and Spain, had fewer comorbidities and lower medication use than hospitalized influenza patients according to a recent study published by the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community. OHDSI has established an international network of researchers and observational health databases...
Trust and Income Inequality Fueling the Spread of COVID-19
Trust in public institutions is linked to fewer COVID-19 deaths, but trust and belonging to groups is associated with more deaths, according to a wide-ranging, McGill-led study of 30-day COVID-19 mortality rates in 84 countries. Greater economic inequality is also associated with COVID-19 mortality. The study led by McGill researchers published in Social Science & Medicine,...