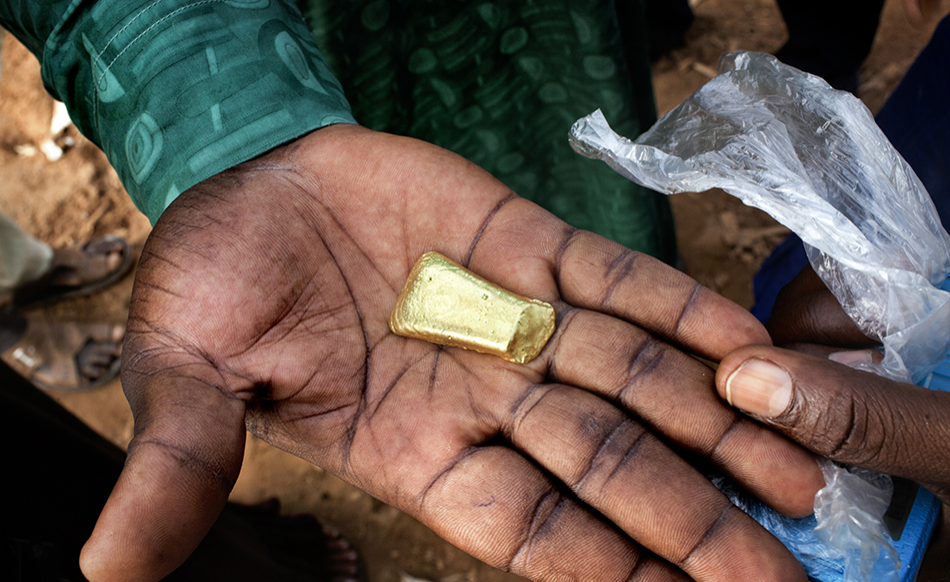

To the west of Ethiopia near the Sudanese border lies a place called the Asosa zone. This may be the location of the oldest gold mine in the world. Dating back some 6,000 years, it provided a key source of gold to the ancient Egyptian empire, whose great wealth was famous throughout the known world. It may even have supplied the Queen of Sheba with her lavish gifts of gold when she visited King Solomon of Israel almost 3,000 years ago.
The excitement in this part of the world is more about the future, however. Some local inhabitants already make a living from prospecting, and several mining companies have been active in the area in recent years, too.
But what comes next could be on a much bigger scale: I have just co-published with my colleague, Owen Morgan, new geological research that suggests that much more treasure might be buried under the surface of this east African country than was previously thought.
Treasure trail
The Asosa zone is made up of flatlands, rugged valleys, mountainous ridges, streams and rivers. It is densely vegetated by bamboo and incense trees, with remnants of tropical rainforests along the river valleys. The zone, which is part of Ethiopia’s Benishangul-Gumuz region, is spotted with archaeological sites containing clues to how people lived here thousands of years ago, together with ancient mining pits and trenches.
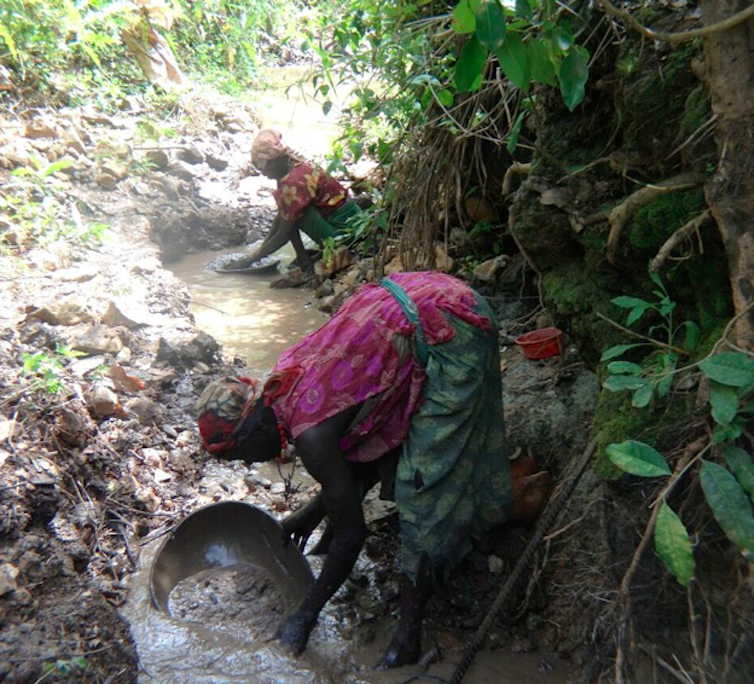
Local inhabitants have long taken advantage of these riches. They pan for gold in Asosa’s streams and also extract the precious metal directly from outcropping rocks.
More substantial exploitation of the region’s riches dates back to the Italian invasion of the 1930s. The Italians explored the Welega gold district in West Welega, south-east of Asosa.
Haile Selassie, emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974, believed the country had the potential to become a global leader in gold. But when the revolutionary Derg government deposed him and the country plunged into civil war, gold mining disappeared off the agenda for a decade and a half. It took until the early 2000s before the government started awarding exploration licences.
Several mines are up and running, neither of them in Asosa. One is at Lega Dembi slightly to the east, owned by Saudi interests. The other, at Tigray in the north of the country, is owned by American mining giant Newmont, and just started production late last year.
More is already on the way: the beneficiary of the Italian efforts from the 1930s in Welega is the Tulu Kapi gold prospect, containing 48 tonnes of gold. This was most recently acquired in 2013 by Cyprus-based mining group KEFI Minerals (market value: roughly US$2.3 billion (£1.7 billion)).
As for Asosa, the Egyptian company ASCOM made a significant gold discovery in the zone in 2016. It published a maiden resource statement that claimed the presence of – curiously the same number – 48 tonnes of gold. Yet this only looks like the beginning.
Au-some potential?
The Asosa zone geology is characterised by various kinds of volcanic and sedimentary rocks that are more than 600 million-years-old. The region has been intensely deformed by geological forces, resulting in everything from kilometre-long faults to tiny cracks known as veins which are only centimetres in length.
Some of these veins contain quartz, and it is mainly here that the region’s gold accumulated between 615m and 650m years ago – along with silver and various other minerals. The gold came from molten materials deep within the Earth finding their way upwards during a process known as subduction, where tectonic forces drive oceanic crust beneath a continent. This is comparable to the reasons behind gold deposits in island arcs like some of the ones in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea.
Our field observations and panning suggest that gold should be generally abundant across the Asoza zone – both in quartz veins but also elsewhere in the schist and pegmatite rocks in which they are located. We also see signs of substantial graphite deposits, which are important for everything from touch-screen tablets to lithium-ion batteries.
There is undoubtedly much more world-class gold within this area than has already been discovered, pointing to a promising source of income for the government for years to come – much of the region remains unexplored, after all. It probably is no exaggeration to say that Ethiopia’s gold potential could rival South Africa’s, which would put it somewhere around the top five gold producing nations in the world.
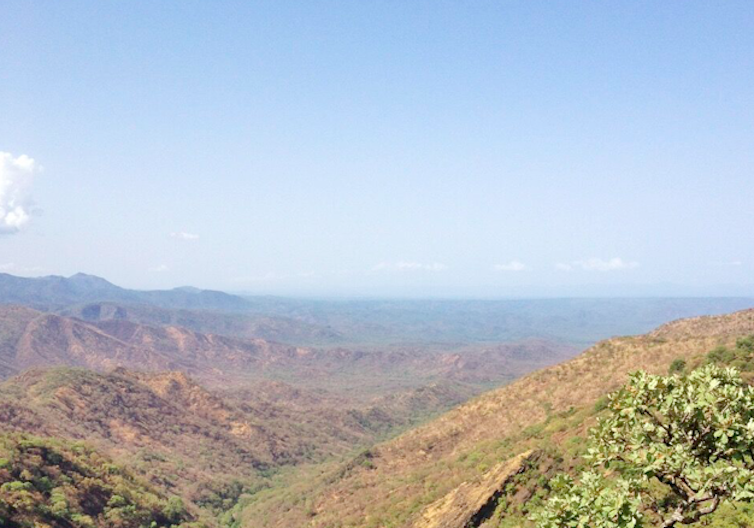

There are still some substantial challenges, however. Dealing with governmental red tape can be difficult. In an area like the Asosa zone there are dangerous wildlife to avoid, such as venimous snakes, baboons and even monkeys. The vegetation also becomes forbiddingly wild during wet seasons.
It is also important to strike up good working relationships with local inhabitants, showing the utmost respect to local cultures – it’s the ethical way to operate, and failing to do so can make life harder with the authorities in the capital. This includes the need to preserve the natural beauty of the region; gold mining already has a very bad international reputation for environmental damage.
With the right approach, however, western Ethiopia will be a literal gold mine that could bring economic benefit to the region. What the Queen of Sheba may have known 3,000 years ago, the modern world is finally rediscovering today.
Liam Bullock, Research Fellow, University of Aberdeen
This article was originally published on The Conversation.



Leave a Reply