A study carried out by the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB) and the Instituto de Saúde Pública of the University of Porto (ISPUP), concludes that exposure to natural spaces during the first COVID-19 lockdown in 2020 was beneficial for the mental health of Spanish and Portuguese citizens....
Health
Teens Experienced Helplessness When Exposed to Secondhand Racism
This past year has been transformational in terms of not only a global pandemic but a sustained focus on racism and systemic injustice. There has been a widespread circulation of images and videos in the news and online. Just like adults, adolescents are exposed to these images with important consequences for their emotional health and...
New Study Shows High Mercury Levels in Indigenous Latin American Women
Women in three Latin American countries who rely on fish for protein and live in proximity to gold mining activity have been found to have elevated mercury levels in their bodies, according to a new study, Mercury Exposure of Women in Four Latin American Gold Mining Countries. The study was conducted by the International Pollutants Elimination Network...
Forget Wearables: Future Washable Smart Clothes Powered by Wi-Fi Will Monitor Your Health
Purdue University engineers have developed a method to transform existing cloth items into battery-free wearables resistant to laundry. These smart clothes are powered wirelessly through a flexible, silk-based coil sewn on the textile. In the near future, all your clothes will become smart. These smart cloths will outperform conventional passive garments, thanks to their miniaturized...
Socially Engaged Older Women More Likely to Be Emotionally Abused or Mistreated
For older adults, participating in social activities can protect against physical and mental signs of aging, but it may also pose risks, especially for women. A new analysis of national data led by University of California – San Francisco (UCSF) found that older women who were broadly engaged in social activities before the COVID pandemic...
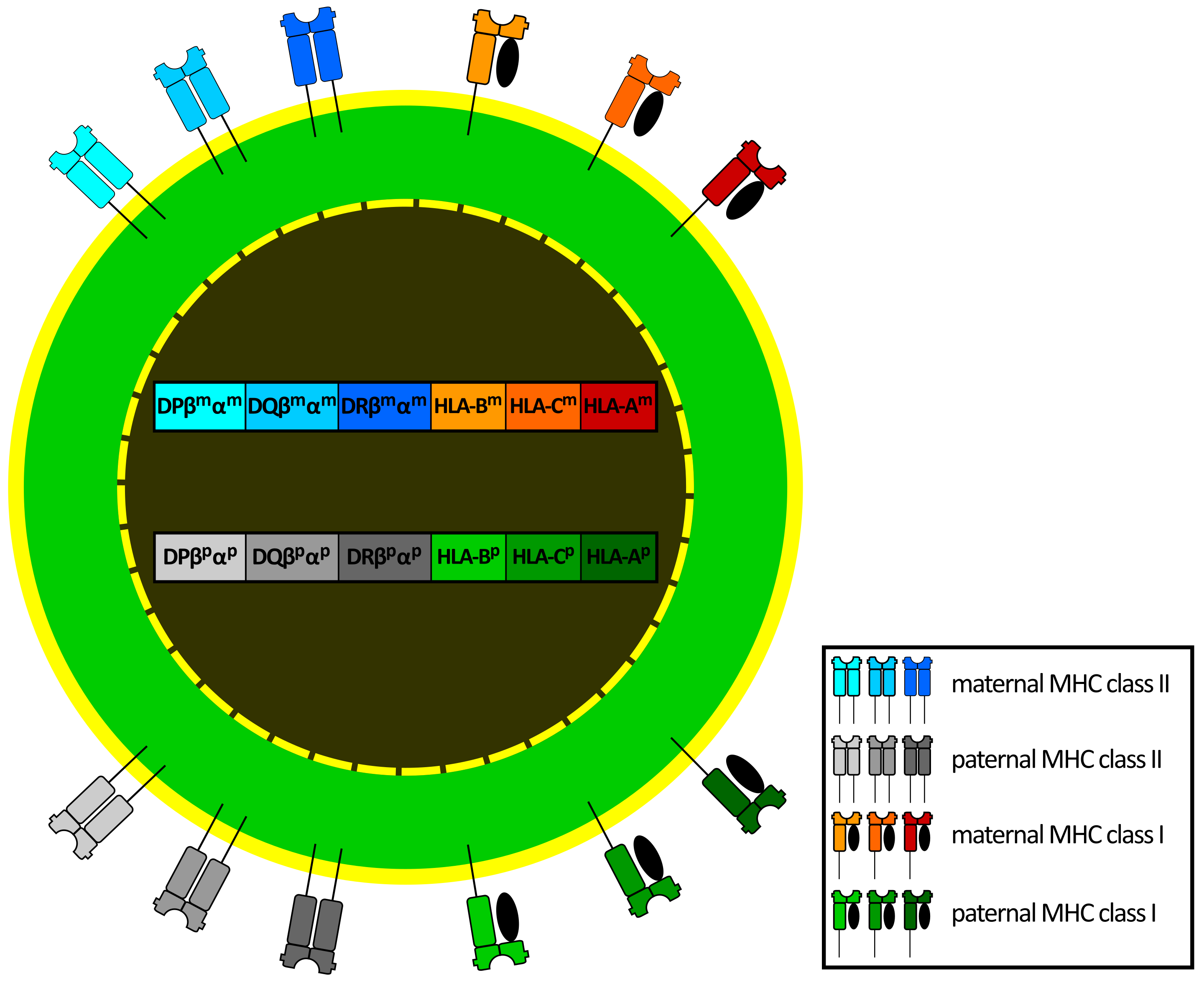
Gene Protection for Covid-19 Identified
The first evidence of a genetic link explaining why some people who catch Covid-19 don’t become sick has been discovered A scientific and medical team led by Newcastle University, UK, has demonstrated that the gene, HLA-DRB1*04:01, is found three times as often in people who are asymptomatic. This suggests that people with this gene have...
Disparities in Covid-19 Rates Among Adults with Kidney Failure in New York City
Among adults with kidney failure undergoing hemodialysis in New York City, Black and Hispanic patients were more likely to develop symptomatic COVID-19 than White patients. Neighborhood-level social vulnerability factors were associated with COVID-19 incidence among White patients, but these factors did not explain racial/ethnic disparities. In an analysis of patients on hemodialysis in New York...
Scientists Can Predict How Well a Stroke Survivor Will Recover Language Skills Using Computer Simulations of the Brain
A team of researchers from Boston University is working to better understand how language and speech is processed in the brain, and how to best rehabilitate people who have lost their ability to communicate due to brain damage caused by a stroke, trauma, or another type of brain injury. This type of language loss is...
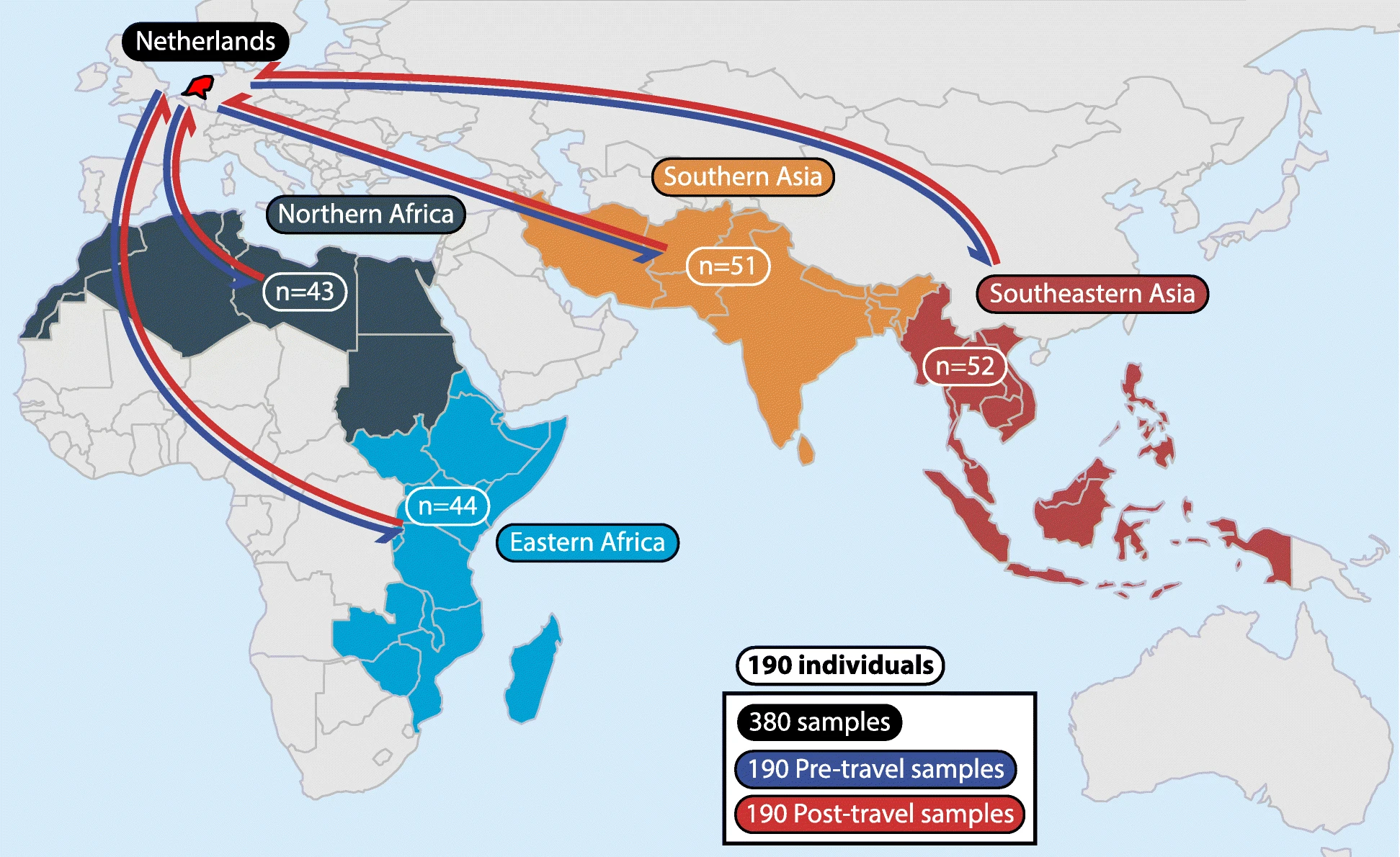
Global Travelers Pick Up Numerous Genes That Promote Microbial Resistance
Carried like stowaways in the guts of international travelers, new and potentially deadly strains of antimicrobial resistant superbugs may be coming to a community near you, suggests new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. “Even before the COVID-19 pandemic, we knew that international travel was contributing to the rapid global increase...
Postpartum Mental Health Visits 30% Higher During Covid-19 Pandemic
Mental health visits for new mothers were 30% higher during the COVID-19 pandemic than before the pandemic, particularly in the first 3 months after giving birth, found new research in the Canadian Medical Association Journal. “Increased visit rates began in March 2020, although the state of emergency was declared only midway through the month, suggesting...