The big idea Undocumented immigration does not increase the violent crime rate in U.S. metropolitan areas. In fact, it may reduce property crime rates. These are the key findings from our recently published article in the Journal of Crime and Justice, co-authored by Yulin Yang, James Bachmeier and Mike Maciag. Research shows that the American...
Author: sp (sp )
Fox News Viewers Write About ‘BLM’ the Same Way CNN Viewers Write About ‘KKK’
It’s no secret that U.S. politics has become highly polarized. Even so, there are probably few living Americans who ever witnessed anything that quite compares with this fall’s first presidential debate. Was it really the case that the nation could do no better than a verbal food fight, with two candidates hurling fourth-grade insults and...
Black Hispanic Individuals Hardest Hit by COVID-19
Results from a new study led by Boston Medical Center (BMC) demonstrate the disproportionate impact of COVID-19 on Hispanic groups within the US, with the most severe outcomes, including death and intensive care, among Hispanic Black individuals. Analyzing data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, researchers found differences between Hispanic groups, with higher...
Researchers Find Confusion Over Masks for Wildfire, COVID-19 Crises
To mask or not to mask – and which mask to use? With public health guidance about masks in the United States confused by political hedging, clarity around mask use is increasingly important, especially as the western U.S. battles the twin crises of wildfire smoke and COVID-19. “The CDC is the gold standard of where...
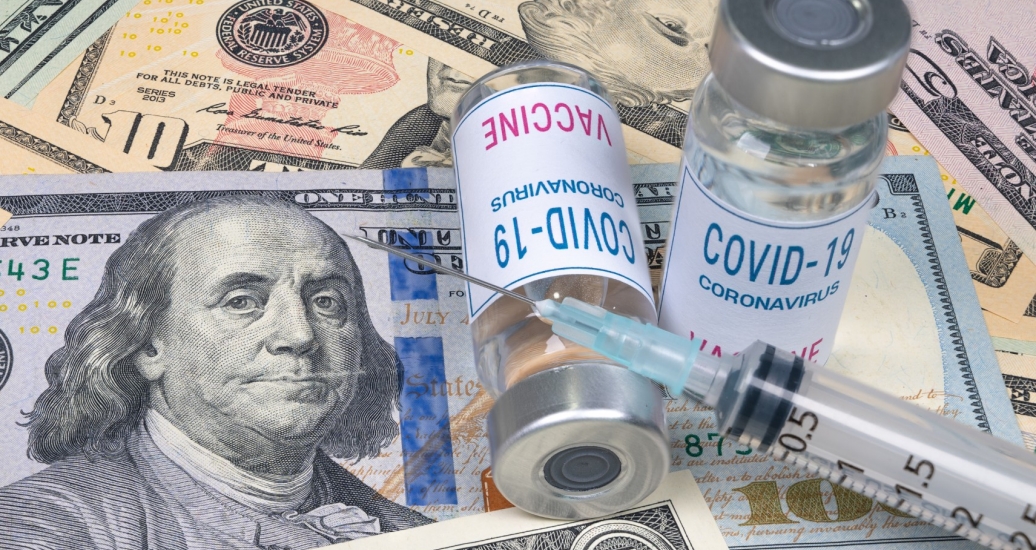
COVID-19 Vaccine Nationalism Could Cost World Up to $1.2 Trillion
Nationalistic behaviour by governments may exclude some countries from gaining access to COVID-19 vaccines and cost the global economy up to $1.2 trillion a year in GDP, according to a new study from the not-for-profit research organisation RAND Europe. If countries demonstrate ‘vaccine nationalism’ – prioritising their own citizens and insisting on first access to...
From Pills to Powder: 1 in 3 High School Seniors Who Misused Prescription Opioids Later Used Heroin
Nearly one-third of students who reported misusing prescription opioids as high school seniors between 1997 and 2000, but did not have a history of medical use, later used heroin by age 35, according to a University of Michigan study. The research also found that 21% of seniors in the same period, who misused prescription opioids and later...
How Initiatives Empowering Employees Can Backfire
Strategies meant to motivate people in the workplace may have unintended consequences — depending on who’s in charge. Recent research from Michigan State University and Ohio State University shows that empowerment initiatives aren’t necessarily the answer for business leaders hoping to motivate their employees. “People tend to think of empowerment in uniformly positive ways,” said...
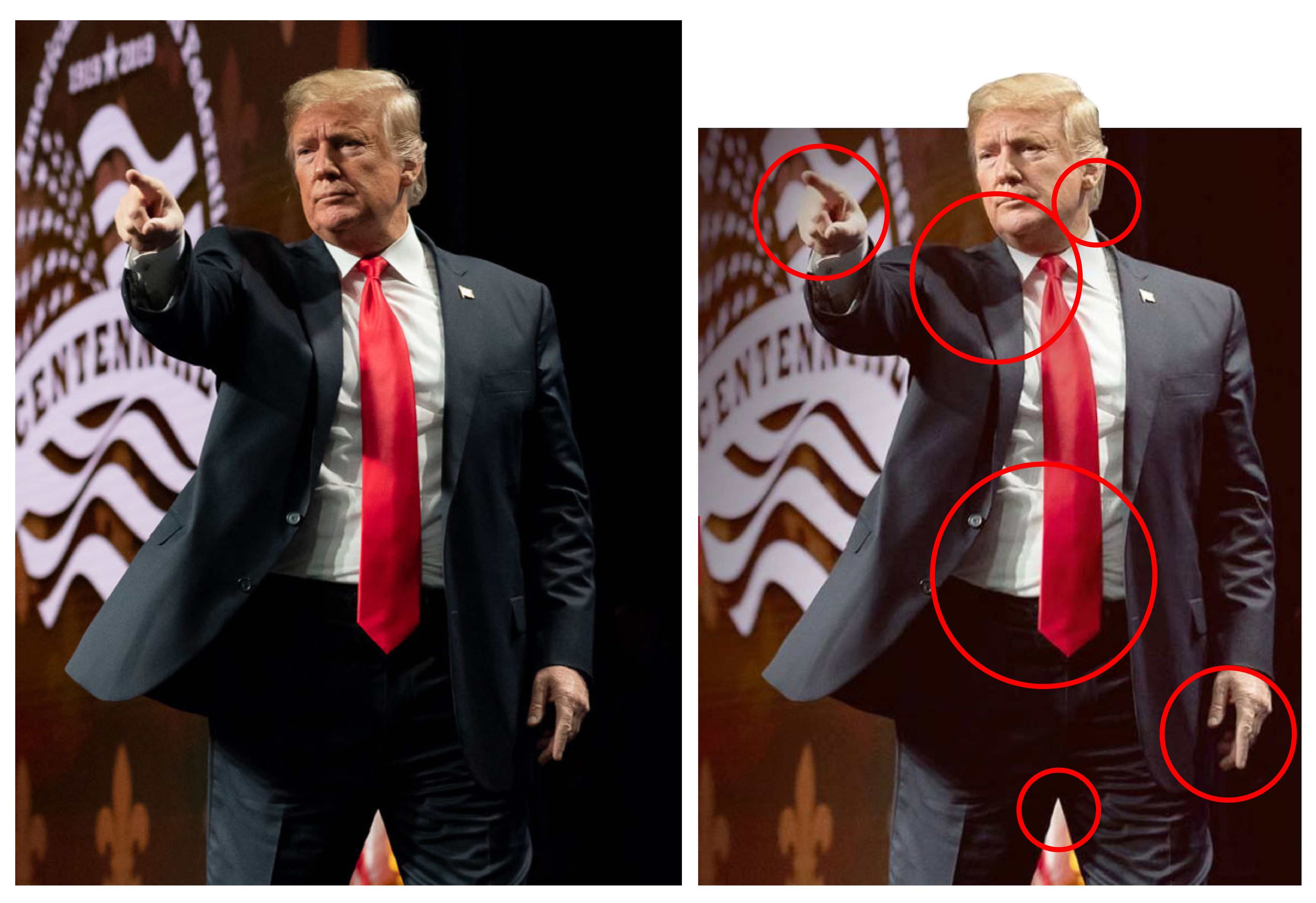
Seeing No Longer Believing: the Manipulation of Online Images
A peace sign from Martin Luther King, Jr, becomes a rude gesture; President Donald Trump’s inauguration crowd scenes inflated; dolphins in Venice’s Grand Canal; and crocodiles on the streets of flooded Townsville – all manipulated images posted as truth. Image editing software is so ubiquitous and easy to use, according to researchers from QUT’s Digital...
The Soft Power Concept of German Energy Foreign Policy
As part of its foreign policy, Germany hopes to promote energy transitions abroad through international energy partnerships. A new study by the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) analyses these bilateral energy partnerships. Building on its reputation as an energy transition frontrunner, Germany is currently pursuing a soft power strategy aimed at winning over foreign...
How Fear Encourages Physical Distancing During Pandemic
Welcome to shopping during the coronavirus pandemic: customers clad in masks, slathered with sanitizer and surrounded by signage urging them to avoid close contact. Despite guidelines plastered on the walls and floors of grocery and retail stores encouraging customers to maintain six-feet of physical distance, many do not. A new study by researchers at the...