Do probiotics prevent gum disease? Is flossing necessary? Many patients are unable to confidently answer these questions and more due to the abundance of conflicting medical information. However, new research led by the University at Buffalo aims to separate fact from fiction in determining which oral hygiene tools actually prevent gum disease. The paper, published...
Author: sp (sp )
Tobacco and Alcohol May Increase Likelihood of Using Illegal Drugs, New Study Shows
The use of legal drugs (tobacco and alcohol) may lead to the use of cannabis, a new study led by the University of Bristol and published in the journal Addiction has found. The study also found evidence that cannabis use may lead to smoking initiation, and opioid dependence could lead to increased alcohol consumption. Additionally, there might be...
Just Because They’re Angry Doesn’t Make Them Guilty: New Research
Computer equipment is missing from a company storage room. Of the three employees who have access, two respond calmly when questioned by management. A third yells and swears. Who is most likely guilty? If you chose the angry one, you’re not alone. New research shows we tend to equate guilt with an angry response to...
Success of Megamusicals Makes Space for Innovation
Megamusicals have often been criticised in the academic world and in the media for their homogenizing tendencies, but increasing academic attention on them is providing us with new insights. In her inaugural lecture at the University of Amsterdam, professor by special appointment of the Musical Millie Taylor will outline the impact of megamusicals on local...
How a Team of Musicologists and Computer Scientists Completed Beethoven’s Unfinished 10th Symphony
When Ludwig von Beethoven died in 1827, he was three years removed from the completion of his Ninth Symphony, a work heralded by many as his magnum opus. He had started work on his 10th Symphony but, due to deteriorating health, wasn’t able to make much headway: All he left behind were some musical sketches....
What Was Really the Secret Behind Van Gogh’s Success?
Before developing his famed “drip technique,” abstract artist Jackson Pollock dabbled in drawing, print making and surrealist paintings of humans, animals and nature. According to a new study from Kellogg School of Management at Northwestern University, this period of exploration followed by exploitation of his new drip technique set up Pollock for a “hot streak,” or...
Meat-Heavy Diets Restricted Hunter-Gatherer Population Sizes
Hunter-gatherer populations with a strong seasonal dependence on meat in their diets had fewer people per square kilometer than those that had abundant plant foods throughout the year. This new result is clear from a study carried out by researchers from the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB),...
How ‘Sissy Men’ Became the Latest Front in China’s Campaign Against Big Tech
The Chinese government has recently taken action against what it calls “sissy men” – males, often celebrities, deemed too effeminate. On Sept. 2,2021, government regulators banned their appearance on both television and video streaming sites. Using the Chinese derogatory slur “niang pao” – literally, “girlie guns” – Chinese cultural authorities explained that they were rolling...
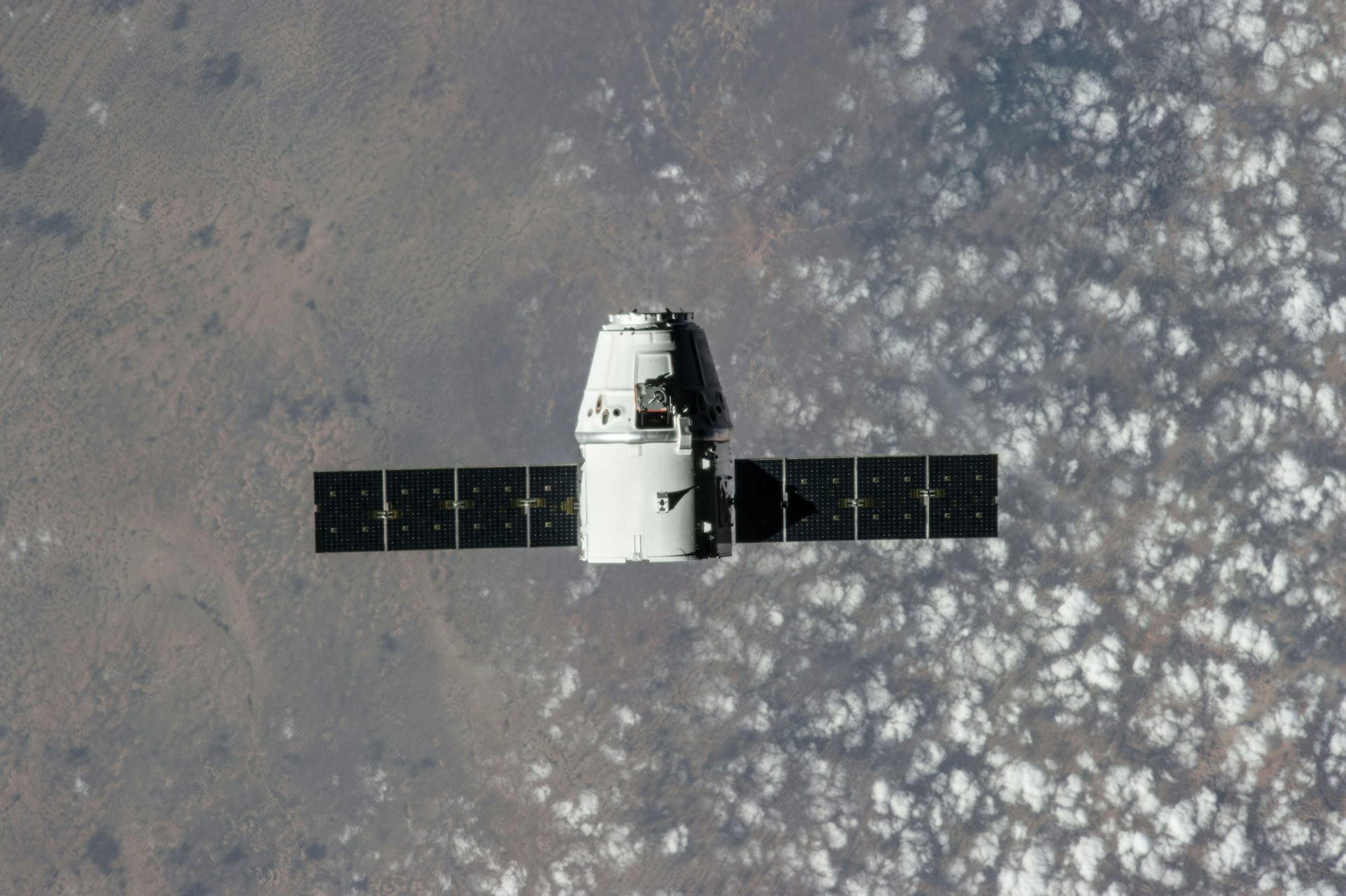
SpaceX Inspiration4 Mission Will Send 4 People with Minimal Training into Orbit – and Bring Space Tourism Closer to Reality
On Sept. 15, 2021, the next batch of space tourists are set to lift off aboard a SpaceX rocket. Organized and funded by entrepreneur Jared Isaacman, the Inspiration4 mission touts itself as “the first all-civilian mission to orbit” and represents a new type of space tourism. The four crew members will not be the first...
Neurodiversity Can Be a Workplace Strength, If We Make Room for It
Emma can recognise patterns within complex code. James can develop several different solutions when faced with complicated problems. But it is unlikely either will find a job where they can put their specialist skills to work — or any job, actually. Emma has dyslexia. James has been diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. These conditions...